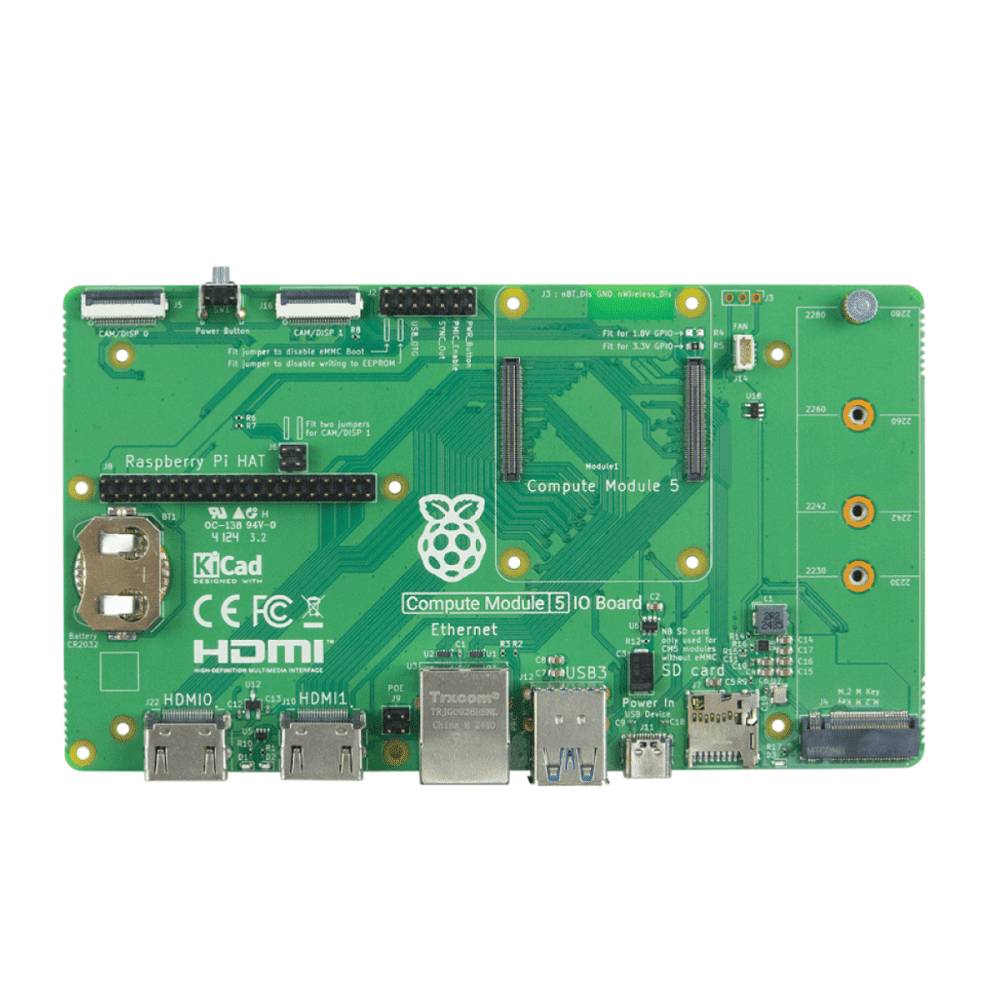
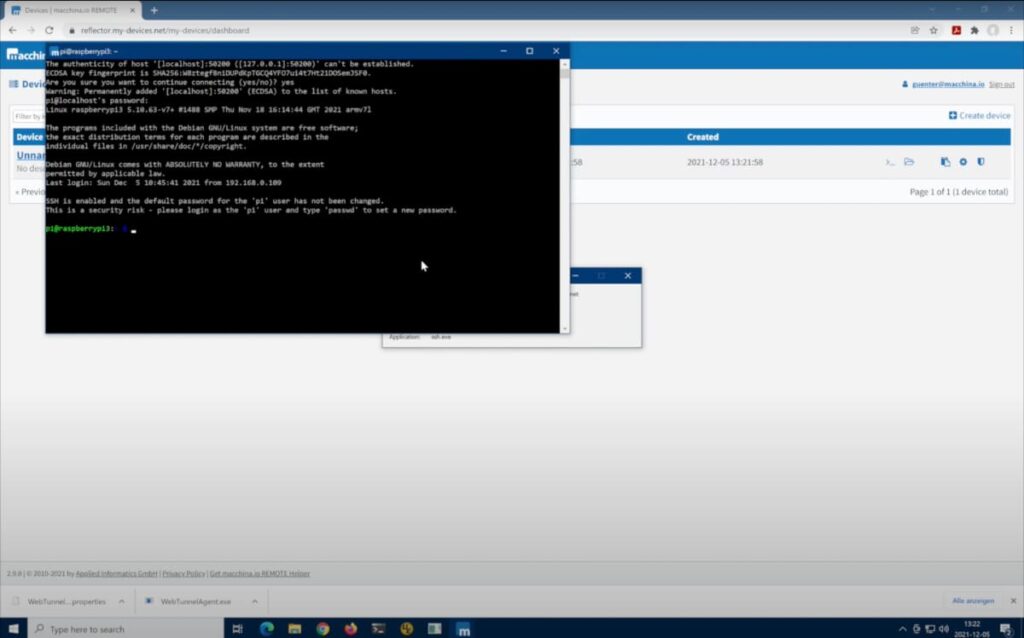
Remote IO Raspberry Pi has become a buzzword in the tech world, especially for enthusiasts looking to create innovative smart solutions. With the increasing demand for remote access and control of devices, Raspberry Pi has emerged as a reliable and affordable platform to build remote IO systems. In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about the best remote IO setups using Raspberry Pi, including hardware configurations, software tools, and practical applications.
Whether you’re a hobbyist, a professional developer, or someone who’s simply curious about IoT technology, this guide will provide valuable insights into how Raspberry Pi can enhance your remote control capabilities. From automating home appliances to monitoring industrial equipment, Raspberry Pi offers endless possibilities for remote IO applications.
In the following sections, we will delve into the specifics of setting up remote IO using Raspberry Pi. We will also discuss the latest trends, tools, and best practices to help you make the most of this versatile device. Let’s dive in!
Read also:The Ultimate Guide To French Onion Dip A Delectable Journey
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Remote IO Raspberry Pi
- Raspberry Pi Overview
- Basics of Remote IO
- Hardware Options for Remote IO
- Software Solutions for Remote IO
- Applications of Remote IO Raspberry Pi
- Step-by-Step Setup Guide
- Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- Security Considerations
- Future Trends in Remote IO
- Conclusion
Introduction to Remote IO Raspberry Pi
Remote IO refers to the ability to control and monitor input/output devices remotely. When combined with Raspberry Pi, this technology opens up a world of possibilities for automation and remote management. Raspberry Pi is a powerful single-board computer that can be easily configured for remote IO applications, making it an ideal choice for hobbyists and professionals alike.
Why Choose Raspberry Pi for Remote IO?
Raspberry Pi is a popular choice for remote IO projects due to its affordability, versatility, and ease of use. It supports a wide range of programming languages and can be integrated with various hardware components, making it suitable for both simple and complex applications. Additionally, Raspberry Pi’s extensive community support ensures that users have access to a wealth of resources and tutorials.
Raspberry Pi Overview
Raspberry Pi is a series of small single-board computers developed by the Raspberry Pi Foundation. Originally designed for educational purposes, it has since gained popularity among developers, hobbyists, and businesses for its versatility and affordability. The latest models of Raspberry Pi come equipped with powerful processors, ample RAM, and a variety of interfaces, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Key Features of Raspberry Pi
- Compact size and lightweight design
- Multiple GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) pins
- Support for Linux-based operating systems
- Built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities
- Expandable storage via microSD card
Basics of Remote IO
Remote IO involves the use of hardware and software to control and monitor devices from a remote location. This can include anything from turning on a light switch to monitoring the temperature of a server room. By using Raspberry Pi as the central hub, users can create a robust and scalable remote IO system that can be accessed via the internet or a local network.
Components of a Remote IO System
- Central controller (Raspberry Pi)
- Sensors and actuators
- Network connectivity (Wi-Fi, Ethernet)
- Software for remote access and control
Hardware Options for Remote IO
When setting up a remote IO system with Raspberry Pi, choosing the right hardware components is crucial. Depending on the specific requirements of your project, you may need to select different sensors, actuators, and interface boards. Here are some popular options:
Popular Sensors for Remote IO
- Temperature and humidity sensors
- Light sensors
- Motion detectors
- Pressure sensors
Actuators for Remote Control
- Relay modules
- Servo motors
- LED strips
- Buzzer alarms
Software Solutions for Remote IO
The software plays a critical role in enabling remote access and control of devices. There are several software options available for Raspberry Pi that can facilitate remote IO operations. These include both open-source and commercial solutions, each with its own set of features and capabilities.
Read also:Scarlett Ohara The Timeless Icon Of Southern Belle Charm And Resilience
Open-Source Software for Remote IO
- Node-RED
- Home Assistant
- OpenHAB
Commercial Software Solutions
- Blynk
- ThingSpeak
- Adafruit IO
Applications of Remote IO Raspberry Pi
Remote IO Raspberry Pi can be used in a variety of applications across different industries. From home automation to industrial monitoring, the possibilities are virtually endless. Below are some of the most common applications:
Home Automation
Control and monitor smart home devices such as lights, thermostats, and security systems from anywhere in the world.
Industrial Monitoring
Monitor and manage industrial equipment in real-time, ensuring optimal performance and reducing downtime.
Agricultural Solutions
Implement smart farming techniques by monitoring soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health remotely.
Step-by-Step Setup Guide
Setting up a remote IO system with Raspberry Pi requires careful planning and execution. Follow these steps to ensure a successful setup:
Step 1: Prepare Your Raspberry Pi
Install the latest version of Raspberry Pi OS and configure the network settings. Ensure that your Raspberry Pi is connected to the internet via Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
Step 2: Connect Sensors and Actuators
Connect the required sensors and actuators to the GPIO pins of your Raspberry Pi. Refer to the datasheets for proper wiring instructions.
Step 3: Install and Configure Software
Install the appropriate software for your remote IO application. For example, if you’re using Node-RED, follow the installation instructions and configure the necessary nodes.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
While setting up a remote IO system, you may encounter some common issues. Here are a few troubleshooting tips:
Issue: Device Not Responding
Solution: Check the power supply and ensure that all connections are secure. Verify the network settings and ensure that the device is reachable from the internet.
Issue: Software Errors
Solution: Review the configuration files and ensure that all settings are correct. Consult the official documentation or seek help from online forums.
Security Considerations
Security is a critical aspect of remote IO systems. Since these systems are often connected to the internet, they are vulnerable to cyberattacks. Here are some best practices to enhance security:
Enable Firewall
Use a firewall to restrict access to your Raspberry Pi and protect it from unauthorized access.
Use Strong Passwords
Ensure that all accounts and services have strong, unique passwords. Avoid using default credentials.
Future Trends in Remote IO
The field of remote IO is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in IoT technology and artificial intelligence. Some of the emerging trends include:
Edge Computing
Edge computing allows data processing to occur closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance.
AI Integration
Integrating AI into remote IO systems can enable predictive maintenance and automated decision-making.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Raspberry Pi is an excellent platform for building remote IO systems. With its powerful hardware, flexible software options, and extensive community support, it offers endless possibilities for innovation. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can create a robust and secure remote IO system that meets your specific needs.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. If you found this article helpful, don’t forget to share it with your friends and colleagues. For more informative content, explore our other articles on IoT and smart technology.